Dr. Kalyan C. Kankanala recently delivered a lecture to the B.Tech – LLB students of UPES School of Law as part of the ‘Patent Law and Practice Program’ being taught by BananaIP Team at the School.
The flow chart below represents the process of post-grant opposition in India.
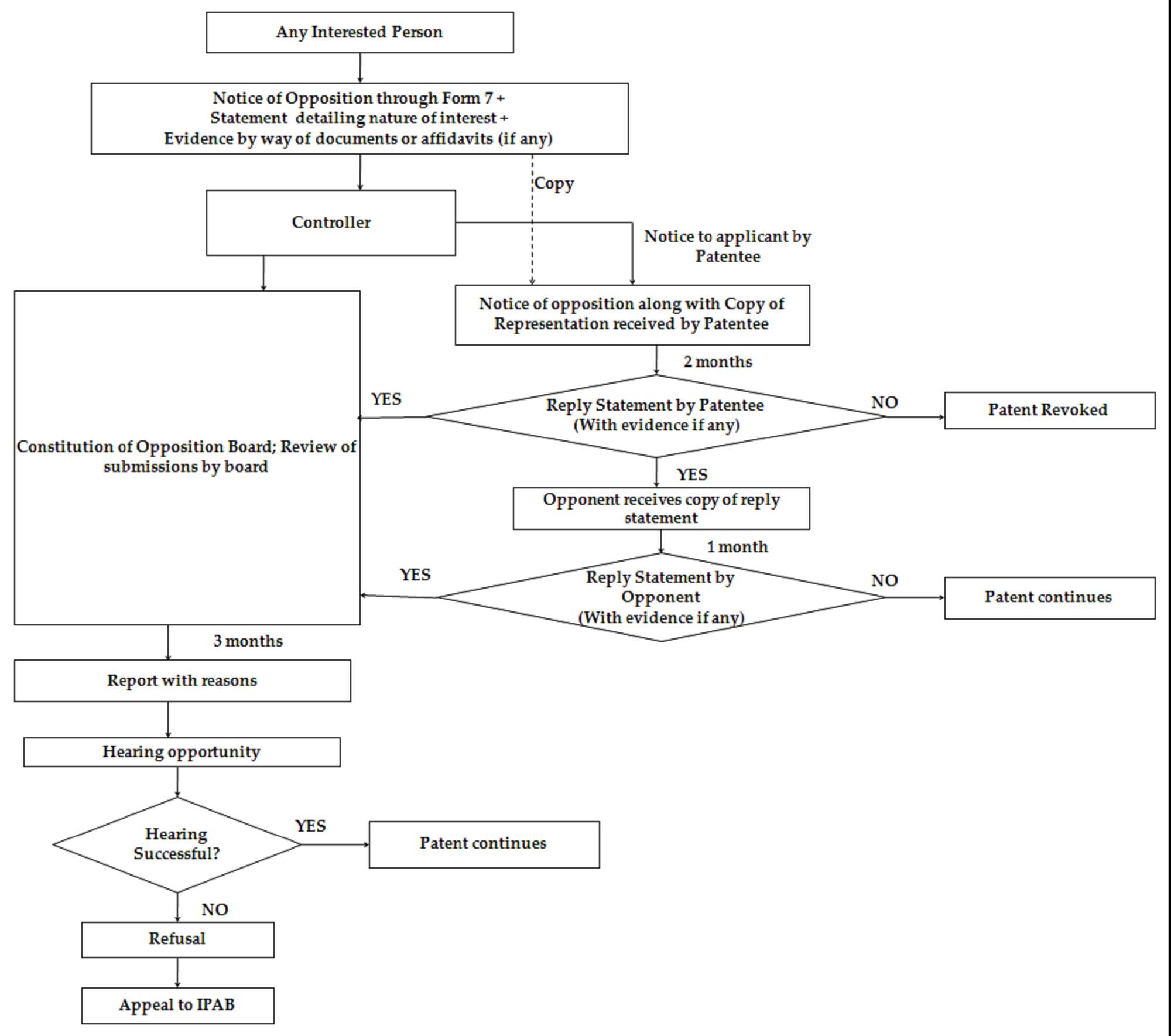
Section 25(2) of the Indian patent (Amendment) Act 2005 provides a provision for filing a post grant opposition against a patent.Under this provision any interested person, may file an opposition against a granted application within one year from the date of publication of grant of the patent.
Post-grant opposition can be made on any of the grounds listed under section 25(2) (a) to (k) of the Patent Amendment Act, 2005:
- Wrongfully obtaining the invention
- anticipation by prior publication
- anticipation by prior date, Prior claiming in India
- Prior public knowledge or public use in India
- Obviousness and lack of inventive step
- non patentable subject matter
- insufficiency of description of the invention
- non-disclosure of information as per the requirement or providing materially false information by an applicant
- Patent application not filed within 12 months of filing the first application in a convention country
- nondisclosure/ wrong mention of source of biological material
- Invention anticipated with regard to traditional knowledge of any community, anywhere in the world.
About Dr. Kalyan C. Kankanala
Dr. Kalyan C. Kankanala manages the largest new age Intellectual Property Firm, BananaIP Counsels, headquartered at Bangalore, India. In addition to helping clients maximize business value from intellectual assets, Dr. Kalyan also consults for United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), and teaches at premier institutions such as National Law School of India University, Bangalore, and Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B).
Featured image source/attribution – here; Governing License – Public Domain



